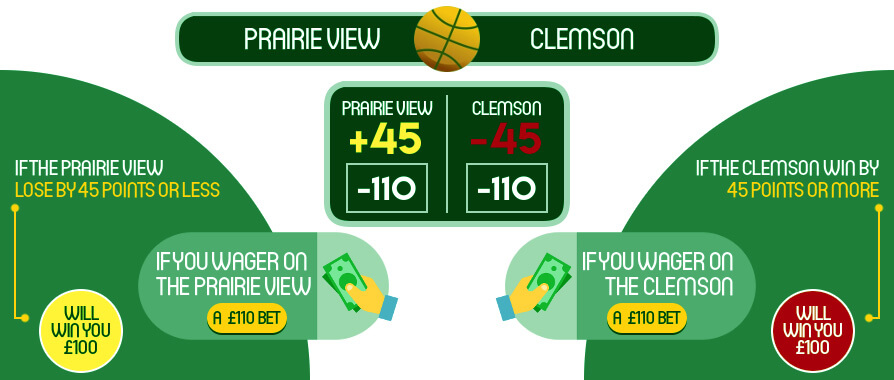
Spread betting is a tax-free way of making profits based on the price movement of various underlying assets, including indices, forex, shares, or commodities. The idea is to predict whether the price of an instrument (asset) will rise or fall in value. The more right you are, the bigger the payout.
In this post, we’re going to introduce you to the concept of spread betting, and show you how it works.
Spread Betting 101 — Basics
Spread betting is defined as a financial derivative that allows you to benefit from the price movement of a financial market. The goal is to speculate the direction in which your chosen market will move in, using the prices offered to you by the broker.
Like in stock market trading, spread bettors are offered two prices — a price at which you can buy (bidding price) and a price at which you can sell (asking price). If you believe that the price of a product will go up, you will buy the price. Conversely, if you expect the asset’s price to decrease in value, you will sell it.
Spread betting allows much greater flexibility for traders than the traditional stock market (buy-and-hold) trading. This is because you can speculate on the prices moving in both directions — up and down, whereas if you were to buy a share, you could only bet that the price will increase.
Since spread betting is technically a bet, it’s not taxed, or in other words, all profits we make from it are ours to keep.
There are a few terms you need to get familiar with to understand how spread betting works:
- Spread
- Bet size
- Bet duration
Spread
The spread is a gap between the buying and the selling price of an underlying asset. The tighter the spread, the better value you’ll get as a trader. On the other hand, if the spread is wider, you’ll have to pay more to open your position.
Brokers will quote their prices in the form of a spread, and the costs of any given trade are taken into account. This means that the bidding price will always be slightly higher than the underlying security, while the asking price will always be below it.
For instance, the FTSE100 might have a spread of two points. That would mean that its buying price will be one point above its current price, while it’s asking (selling) price will be one point lower.
Bet Size
Bet size is another significant aspect to spread betting. It refers to the amount of money you want to bet per point of movement of the underlying asset. You can choose your own bet size as long as it suits the minimum the broker accepts for that market.
Spread betting movements are expressed as points. These points can be measured in euros, cents, or even fractions of a cent, depending on the liquidity and volatility of your chosen market. You can find what unit the points are measured in by clicking on the dealing ticket.
For every point that the market rises or decreases in value, you’ll make or lose money, respectively. More specifically, your net profit or loss is calculated by multiplying the stake and the difference between the opening price and the closing price of the market.
For example, if you bought Facebook shares at €1 per point, and they increase by 100 points, you would bank €100 if you were to close the spread bet at that point. Conversely, if the market price moved 100 points against you, you would lose €100. For every point the market price rises, buy spread bettors would earn €1; and for every one-point drop, spread bettors that placed the sell bet would earn €1.
Bet Duration
The bet duration is the length of time during which the bet is valid. Every spread bet is valid only for a limited timespan. The fixed timescale of your contract or position can be anywhere from one day to several months. You can close your bet at any point during the designated timescale, provided that the spread bet is open for trading.
There are two types of bet durations relevant in spread betting:
- Daily funded bets — These feature the narrowest spread and last as long as you decide to keep them open. Daily funded bets are subject to overnight funding, which makes them more suitable for short-term positions.
- Quarterly bets — As the name suggests, quarterly bets expire at the end of the current quarter (or the quarter of your choosing). These represent a futures bet with the funding costs factored into the spread. The spread on this type of bet is smaller, and the funding costs are lower (no daily interest is paid), which makes them more profitable for long-term predictions.
Spread Betting Leverage
Leverage is one of the major selling points of spread betting as it provides the possibility of opening a position with just a fraction of the underlying asset’s value. Unlike traditional share trading, where you would have to purchase the full value of your investment up front, in spread betting, you can put up a small amount of money (a percentage of the full value) and yet control a much bigger value. The sum difference is provided as leverage by the broker.
For example, when placing a spread bet on stocks, you might have to put up 10% of the total value of the price. That would mean that the given market has a 10:1 leverage factor. Other markets may have higher or lower leverage.
Leverage is a double-edged sword. It can significantly amplify your profits or losses as they are calculated based on the trade’s total value, not the initial stake. And while this presents a potentially very lucrative opportunity, it’s important to keep in mind that the potential losses are also magnified. That’s why spread betting requires an effective risk management strategy.
Spread Betting Margin
Margin refers to the amount of deposit required to open a position. The margin accounts for only a small fraction of the total trade’s value. Oftentimes, leveraged trading is also called trading on the margin.
There are two distinctive types of margins that you should know about:
- Deposit (initial) margin — The initial margin is the amount of money that you need to put down to open the trade. This sum will be enough to start trading and cover the losses and price swings.
- Maintenance margin — If the trade is going against you, you may be required to put in additional funds to cover losses that are not covered by the initial margin. Typically, when things go south, you’ll get a margin call (notification) from your broker, asking you to invest more funds, or risk losing your position.
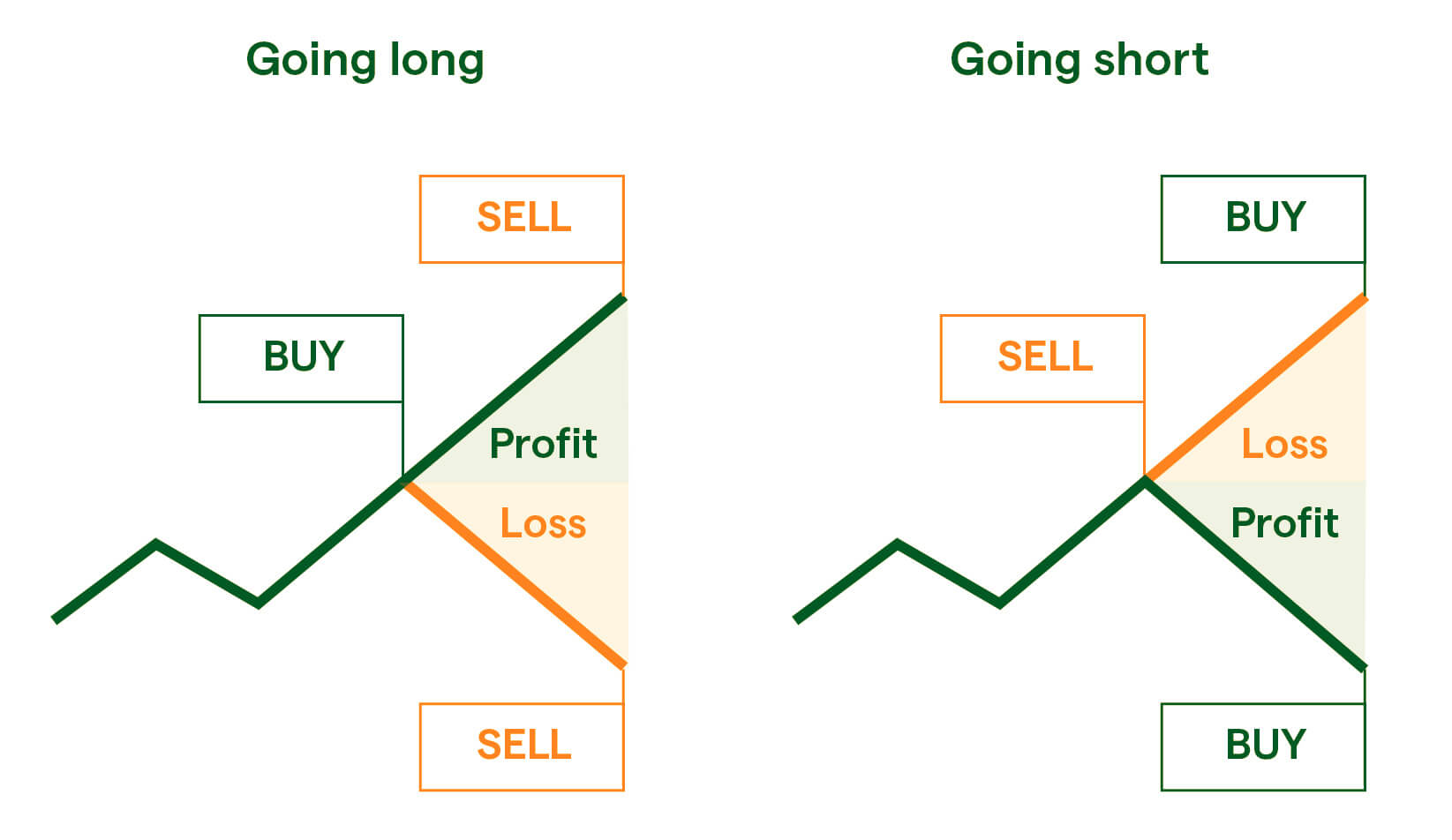
Going Long and Short in Spread Betting
This is a significant advantage spread betting has over traditional stock market trading. When buying and selling shares, you can buy them, and profit if the share value rises. With spread betting, you can make a profit even if the market value decreases. In other words, you can go both long and short.
For example, if you believe that the company will go bust, you can go short, opening the sell position. The more the company’s value plummets, the bigger your payoff will be. On the other hand, if you’re expecting a certain company’s shares to rise, you can go long and buy the bet. The more the company’s price goes up, the more profit you’ll make.
Bottom line — your potential profit depends on the accuracy of your predictions and the size of your opening position.
Spread Betting Example
Let’s assume that Google’s shares are traded at a selling price of 24322 (€243.22) and a buying price of 24290 (€242.90). You expect the shares to increase in the next couple of days and decide to go long (buy) them for €10 per point of price movement at 24290.
If your predictions are accurate, and Google’s shares go up, you can decide to close your trade when the buying price hits 24390. In this case, the market has gained 100 points (24390-24290), so your trade would earn you a tax-free profit of €1000 (100 x €10).
This seems like easy money, but you could have just as easily lost a thousand euros. If the market had plummeted in value down to a selling price of 24190, you would have lost €1,000. That’s without counting the additional charges.
Spread Betting Risk Management
Spread betting is a classic high risk – high reward venture where you can win big overnight or go broke in a flash. That’s why you must create an efficient risk management plan and stick to it. This plan should factor in the risks you face when trading and provide an appropriate emergency exit.
Stops are key tools for managing your budget. When you set a stop on an open position, you’re telling your spread betting provider to pull you off the trade if the price movement starts going against you. Put differently; a stop will limit your risk, by setting a maximum loss you can encounter on a given position.
There are two types of stop-loss orders:
- Standard stop-loss order — Automatically closes out a losing trade once the market reaches a set price level. With standard stop-loss orders, your trade can be closed out at a worse level than the stop trigger. This can occur when the market is in a state of high volatility.
- Guaranteed stop-loss order — This type ensures that you close your losing trade at the exact value you have set, regardless of the underlying market factors. However, this form of stop-loss order usually costs more than the standard version.
Benefits of Spread Betting
Spread betting is popular with traders for a variety of reasons. These include:
- Tax-free — You get to keep all profits you make from spread betting since it’s not subject to Capital Gains Tax. Since spread betting is classified as gambling by the UK Government, you don’t have to pay Stamp Duty either.
- Fee-free — Spread bets are exempt from any commission charges you may face when you trade shares with a stockbroker.
- Leveraged product — You can control a huge value trade with a small deposit.
- Going long or going short — Spread betting allows you to profit from a descending market value, which isn’t possible with stock market trading.
- Round-the-clock trading — You can place spread bets 24/7 on a variety of commodities and treasuries. This is a huge advantage over sports betting per se.
- Thousands of unique markets — With spread betting, you get to choose between thousands of different markets from various categories. These include ETFs, forex, cryptocurrencies, treasuries, commodities, and indices.
- Trade wherever you are — Spread betting platforms are accessible via a wide range of desktop and mobile devices. You can open a trade from your PC, and close it later on while commuting from work via your iOS or Android mobile phone.
Sports Spread Betting
Sports spread betting is a combination of traditional sports betting and financial spread betting.
In traditional sports betting, also known as fixed-odds betting, you place a wager at odds predetermined by the bookie. If the bet wins, your net profit is calculated by multiplying the odds with the stake. This an all-or-nothing bet — you can either predict a certain outcome or not. In other words, you either win a fixed amount of cash or lose whatever amount your stake was.
In contrast, sports spread betting provides a wide variety of wagers on whether a specific variable in a sporting contest will go above or below the spread indicated by your sports spread betting platform.
In the context of sports spread betting, the spread refers to the buy-sell range. For example, the spread for total goals scored in a football match could be 1.8-2.0. If you believe that there would be a goal-fest in the given match, you will buy. Conversely, if you’re predicting a low-scoring match, you would sell.
Like in financial spread betting, the payoff is determined by the accuracy of your bet and the stake. If you buy at €10 per point (per goal in this scenario), you will earn profit for every goal scored past the 2.0 threshold. For example, if the match result is 2:2 (4 goals in total), you would win €20 of tax-free profit.
You can place sports spread bets on various sports, including horse racing, football, cricket, tennis, and so forth.
Bottom Line
Spread betting can be extremely profitable if it is utilized correctly and with care. It’s ideal for traders who want to try making huge profits with a small investment. Keep in mind that spread betting comes with significant risks, and it’s not for the faint-hearted. That’s why here at Betopin we strongly suggest that you learn all the intricacies of spread betting before getting in on the action. Hopefully, this page has provided you with the fundamentals to help you get started.